At x -13 y 4x 3 2x 2 1 -427 29 1 2927 Therefore the function has a maximum value at -13 2927. In the above example the firm maximizes its profits when it produces 7 units because it is where MC equals MR.

Profit Maximization In A Perfectly Competitive Market Microeconomics
The profit-maximizing choice for the monopoly will be to produce at the quantity where marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost.
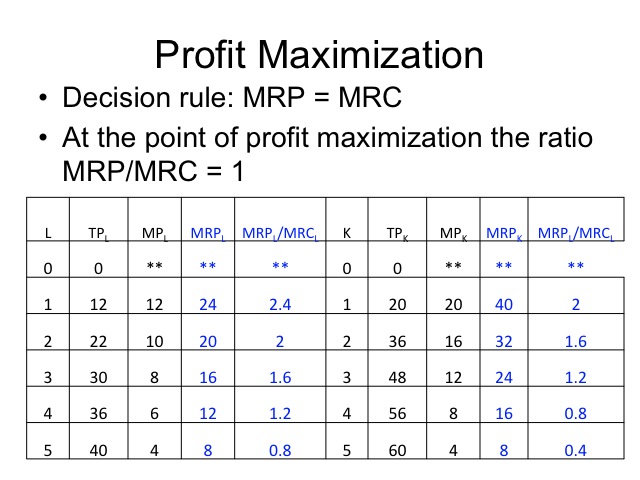
. Table 11 In this post step 5 states the profit-maximizing output level is quantity 5. The profit-maximizing choice for the monopoly will be to produce at the quantity where marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost. Cartels imply direct although secret agreements among the competing oligopolist with the aim of reducing the uncertainty arising from their mutual interdependence.
The first order condition states that the first derivative of profit must be equal to zero. But in this case p 28 M C 30 p M C. Profit maximisation for a monopoly.
The first column shows the quantity of output in bushels and the second column shows Jennifer and Jasons total revenue from their output. In Step 1 the monopoly chooses the profit-maximizing level of output Q 1 by choosing the quantity where MR MC. For each increment calculate total profit by subtracting total costs from total revenue.
In this diagram the monopoly maximises profit where MRMC at Qm. The firm doesnt make a profit at every level of output. Figure 1 shows total revenue total cost and profit using the data from Table 1.
If the monopoly produces a lower quantity then MR MC at those levels of output and the firm can make higher profits by expanding output. This is Q 40. We start by identifying the profit-maximizing level of output where marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
ΔRΔq MR and ΔCΔq MC. This rule can be derived algebraically. Hence the profit-maximizing condition is met.
That is MR MC. In Step 2 the monopoly decides how much to charge for output level Q 1 by drawing a line straight up from Q 1 to point R on its perceived demand curve. The vertical gap between total revenue and total cost is profit for example at Q 60 TR 240 and TC 165.
We can find the profit-maximizing output using the MR MC condition. The market value of their output. If so both q 4 and q 5 the profit is 40.
Profit Total Revenue TR Total Costs TC. Find y on the lower graph and follow the vertical line to y on the upper one. We know Π TR- TC Taking its derivative with respect to Q Π Q TR Q -TC Q 0 This condition holds only when TR Q TC Q TR Q provides the slope of the TR curve which in turn gives MR.
Find the corresponding y-coordinates for the x-value maximum you found in Step 2 by substituting back into the original function. Profit-maximizing outputis y because that is the point at which the distance between total revenue and total cost is greatest andtotal revenue is greater than total cost. Data in Table 531 to find their profit-maximizing level of output.
One way to find the profit-maximizing quantity would be to take the derivative of the profit formula with respect to quantity and setting the resulting expression equal to zero and then solving for quantity. We need to write expression for MR MC and then solve for Q. Thus the monopoly will charge a price P 1.
Profit πTR- TC is maximised where increment of output leaves profit unchanged. Besides how do you calculate profit maximizing output in Monopoly. Step 4 states the output level where price equals the marginal cost is the output level that maximizes profits.
The price is 16 which you can read off the demand curve for quantity equals 40. The difference is 75 which is the height of the profit curve at that output level. If the monopoly produces a lower quantity then MR MC at those levels of output and the firm can make higher profits by expanding output.
P 150 3 143 107 You can verify that at this output MR MC 6417. That is MR MC. However after the output of 5 the marginal cost of the output is greater than the marginal revenue.
By plugging the value of Q in the demand function we get price P 107. The rule is that profit is maximised when MR MC holds for all firms whether competitive or not. ΔπΔq ΔTRΔq ΔTCΔq 0.
ATC at this quantity is 2571. The vertical distance from the demand curve to the average total cost curve represents the firms. Therefore profit maximisation occurs at the biggest gap between total revenue and total costs.
If we use a market price of 31 and the cost data from the table above and plot this data we get. You will use this column to verify that total profit is maximized where marginal costs equal marginal revenue. A firm can maximise profits if it produces at an output where marginal revenue MR marginal cost MC Diagram of Profit Maximisation To understand this principle look at the above diagram.
Cartels aiming at joint-profit maximization. Total revenue TR is equal to the market price. Calculate total profit.
MR MC MR 90 4Q MC 4Q 10 Q 10 The profit-maximizing output can also be determined from the intersection of marginal revenue and marginal cost curves. You can tell the same story from the bottom graph but using the marginal costprice terminology. This is the 2nd of 6 videos going through an exam-type question on using quadratic and linear functions to solve business matheconomics problems.
In this particular case the aim of the cartel is the maximisation of the industry joint profit. 150 6Q 03Q 2 4Q 60 In the above expression Q 143. Next look for the profit margin the difference between price and average cost.
For each increment subtract the change in total revenue. This means the firm will see a fall in its profit level because the cost of these extra units is greater than revenue. Thus we conclude that profit is maximised when MR q MC q.
Why it is the profit-maximizing output level.
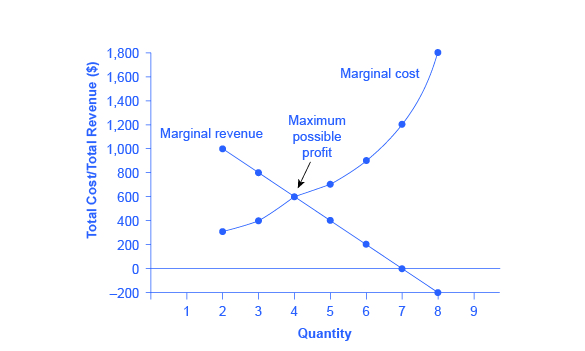
12 2 How A Profit Maximizing Monopoly Chooses Output And Price Principles Of Microeconomics Scarcity And Social Provisioning

How To Calculate The Profit Maximizing Level Of Output Youtube

0 Comments